What Is SAP ECC? | A Comprehensive Guide
What Is SAP ECC?
Ever feel like your business is a bit… disorganized? Like you’re juggling a million things and just waiting for one to drop? Well, that’s where SAP ECC comes in. Essentially, it’s a central nervous system for your business, a suite of software designed to integrate all your core processes. Think of it as the digital glue that holds everything together, from finance and human resources to manufacturing and supply chain. It’s a comprehensive system aimed at streamlining operations and improving decision-making. But more than just glue, SAP ECC provides the tools for data provisioning – pulling data from your various business areas into one accessible spot.
What does ECC stand for anyway?
It stands for Enterprise Central Component, which, honestly, is a bit of a mouthful. But the name does give you a clue as to what it does. SAP ECC is the core or “central” component of the SAP Business Suite. This is achieved via data provisioning adapters. These adapters give you access and allow interaction with your SAP ECC data and metadata. Think of it as giving you the keys to unlock all the useful information hidden within your business.
Imagine you’re running a bakery (because who doesn’t love thinking about pastries?). SAP ECC would help you track everything from ingredient inventory (how much flour you have left), to production schedules (how many croissants you need to bake), to sales and customer orders (that rush for sourdough on Saturday mornings). All this information is centralized, giving you a complete picture of your business in real-time. No more guessing, no more frantic phone calls, just data-driven decisions. Sounds good, right?
Why All the Buzz Around SAP?
SAP (Systems, Applications & Products in Data Processing) itself has been around for ages, and you’ve probably heard the name thrown around. But why is it such a big deal?
Well, let me tell you, SAP didn’t become a global leader by accident. What started with a small group of ex-IBM employees in Germany back in 1972, now dominates the ERP software market. SAP’s products are comprehensive, customizable, and, frankly, just really, really powerful. They allow companies – big and small – to manage their business processes with efficiency and insight.
And that’s the key – insight. It’s not just about automating tasks; it’s about providing the information you need to make smarter decisions.
Digging Deeper: The Modules That Make it Tick
Okay, so SAP ECC is a “suite,” but what does that actually mean? It’s broken down into modules, each handling a specific area of your business. Here are a few of the big players:
-
Financial Accounting (FI) & Controlling (CO) – FICO: This dynamic duo handles all things financial! We’re talking financial accounting, reporting, and cost planning. FICO enables organizations to manage and store every shred of their financial data and transaction history in one place, and then, to top it off, run financial analytics. It’s basically your financial command center.
-
Sales and Distribution (SD): Need to manage your sales processes? SD’s got you. This module manages major processes of sales and distribution, from selling products directly or through distribution networks to handling customer returns, billing, and credit issuance. It’s all about getting those products into the right hands, efficiently.
-
Materials Management (MM): Managing materials and services? MM steps up. This module manages procurement of materials and services from suppliers as well as related inventory processes, like counting inventory and reconciling it. It even manages goods issuance, receipts, and transfers of material.
-
Production Planning (PP): Now, planning production is no easy feat. This module helps businesses align demand with manufacturing capacity so they can more effectively plan product manufacturing, sales, and distribution. PP plays a vital role in a manufacturer’s supply chain and can be used for discrete, process, repetitive manufacturing, or a combo of multiple types.
-
Quality Management (QM): Ensuring top-notch quality across the board? Then here’s QM. It integrates with procurement, production, sales, and equipment maintenance processes. It has some super advanced features too, like complete internal or external audits. QM also assists in finding root causes of product failure to ensure ongoing quality improvements to a company’s business processes.
-
Plant Maintenance (PM): Keeping things running smoothly? PM to the rescue. This module monitors machines and functional locations, such as a chiller room or boiler room, to ensure proper working order. It provides alerts when issues are detected to prevent machine failures and production disruptions. The SAP PM component covers business processes such as preventive, corrective, and refurbishment maintenance. It’s the guardian of your operational uptime.
-
Customer Service (CS): Serving customers with excellence? CS swoops in. This module handles the business processes for providing maintenance services to customer equipment, and the option to bill customers for the maintenance services delivered. Happy customers are repeat customers, after all!
-
Project System (PS): Handling those large, complex projects? PS makes the chaos manageable. This module is meant to manage large, complex projects such as setting up a new manufacturing plant or monitoring a plant’s maintenance turnaround. Funneling all project-specific procurement or production through PS ensures that this module can allocate a project’s costs correctly while keeping them within the budget.
-
Human Capital Management (HCM): Managing your workforce effectively? HCM’s got your back. This module manages HR-related functions. This includes payroll, time management activities such as attendance and leave, career development, travel, and workplace safety. Because a happy, healthy, and well-managed workforce is a productive workforce.
Each of these modules can be used independently or integrated with others, depending on your specific needs. The flexibility is a huge selling point.
From SAP ECC to S/4HANA: The Evolution (Detailed Comparison)
Now, here’s where things get interesting. You might hear people talking about SAP ECC and then immediately hear the term S/4HANA thrown around. So, what’s the deal?
SAP ECC was the flagship ERP system for a long time, but SAP has since developed a newer, more advanced version called S/4HANA. But before we dig into S/4HANA, let’s clear up some terminology. SAP documentation officially changed from using the term module to using the term component when it moved from R/3 to SAP ECC, but many in the industry still use the term module. So both module and component usually refer to parts of the program.
To start, let’s define the difference between SAP ECC and SAP ERP. The term SAP ERP is SAP’s catchall for its various ERP products, including ECC, S/4HANA, Business One and Business ByDesign. Although SAP ERP is used as a catchall, SAP ECC is the set of core modules typically used in SAP ERP.
Next, let’s talk HANA. SAP HANA is an in-memory database for processing high volumes of data in real time. Meanwhile, SAP ECC is an ERP system and Business Suite’s core. ECC is an application suite that runs on a database, of which HANA is one example. When ECC is run on HANA it’s called Suite on HANA. The full name is SAP Business Suite powered by SAP HANA.
Think of SAP ECC as the trusty old car that’s been reliable for years. It gets you from point A to point B, but it’s not exactly cutting-edge. S/4HANA, on the other hand, is like the sleek, new electric vehicle. It’s faster, more efficient, and packed with the latest technology.
S/4HANA is built on SAP’s in-memory platform, HANA, which allows for real-time data processing and advanced analytics. This means you can get insights faster and make decisions more quickly. It also offers a more streamlined user experience and is designed to be more flexible and adaptable to changing business needs.
But the differences don’t stop there. Here’s a head-to-head comparison:
-
Database: SAP ECC can run on various databases, including Oracle, IBM DB2, and Microsoft SQL Server. S/4HANA, however, only runs on the HANA database. This is a key difference that allows S/4HANA to leverage the in-memory capabilities of HANA for faster processing and real-time analytics.
-
Deployment: S/4HANA offers more deployment options than SAP ECC. While ECC is primarily deployed on-premises, S/4HANA can be deployed on-premises, in the public cloud, in the private cloud, or in a hybrid environment. This gives businesses greater flexibility in choosing the deployment model that best suits their needs.
-
User Experience: S/4HANA uses the SAP Fiori user experience (UX), which is a modern, intuitive, and mobile-friendly interface. SAP ECC uses an older, standard GUI, which can feel dated and less user-friendly in comparison. Fiori is designed to be more accessible and easier to use, even for casual users.
-
Advanced Functions: S/4HANA incorporates more advanced technologies, like robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning (ML), and artificial intelligence (AI). These advanced capabilities aren’t available in SAP ECC. S/4HANA is designed to be a more intelligent and automated ERP system, helping businesses to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make better decisions.
SAP is pushing companies to migrate to S/4HANA, and support for ECC is gradually being phased out. The transition includes assessment, a migration strategy, project preparation, system conversion, data migration, testing, system configuration, and go-live monitoring. SAP promises to support SAP ECC and other core Business Suite 7 applications until 2027, with optional extended maintenance until the end of 2030. Organizations still using ECC should begin planning a migration to S/4HANA or other ERP systems now! Unless an organization opts for the extended maintenance option, support updates and security patches for ECC will stop in 2027.
So, if you’re still running on ECC, it’s definitely time to start thinking about your migration strategy.
Why Should You Care About Any of This?
Okay, so all this tech talk can be a bit overwhelming, I get it. But here’s why you should care about SAP ECC (or, more likely, its successor S/4HANA):
-
Increased Efficiency: Streamlining your business processes leads to increased efficiency and reduced costs. You will also track financial performance, track sales volumes, and oversee the distribution of products with the efficient software suite.
-
Improved Decision-Making: Real-time data and advanced analytics empower you to make smarter decisions.
-
Better Customer Service: Integrated processes and improved visibility allow you to provide better customer service.
-
Enhanced Collaboration: SAP ECC facilitates collaboration across departments and locations.
-
Greater Agility: The system’s flexibility allows you to adapt to changing business needs quickly.
-
Competitive Advantage: In today’s fast-paced business environment, having a robust ERP system like SAP ECC can give you a significant competitive advantage.
Basically, it’s about running your business better, faster, and smarter. And who doesn’t want that? Plus, SAP 4/HANA is updated every two years, so this system is constantly improving!
Is SAP ECC Right for Your Business?
That’s the million-dollar question, isn’t it?
The truth is, SAP ECC (and S/4HANA) isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution. It’s a powerful tool, but it’s also complex and can be expensive to implement.
Here are a few things to consider:
-
Size of Your Business: SAP ECC is generally better suited for mid-sized to large enterprises. Smaller businesses may find it too complex and expensive.
-
Complexity of Your Processes: If your business processes are relatively simple, you may not need all the bells and whistles of SAP ECC.
-
Industry: Certain industries, such as manufacturing and finance, tend to benefit more from SAP ECC than others.
-
Budget: Implementing and maintaining SAP ECC can be a significant investment. Make sure you have the budget and resources to support it.
-
Future Growth: If you’re planning to expand your business, SAP ECC can provide the scalability you need to support that growth.
If you’re a small startup just selling handmade jewelry on Etsy, SAP ECC is probably overkill. But if you’re a multinational corporation with complex supply chains and global operations, it could be exactly what you need.
The Challenges of SAP ECC (Let’s Be Real)
Alright, let’s keep it 100. Implementing and running SAP ECC isn’t always a walk in the park. There are challenges, and it’s important to be aware of them:
-
Complexity: SAP ECC is a complex system, and it takes time and effort to learn how to use it effectively. There’s a steep learning curve, no doubt about it.
-
Cost: As mentioned earlier, SAP ECC can be expensive to implement and maintain. You need to factor in the cost of software licenses, hardware, implementation services, and ongoing support.
-
Implementation Time: Implementing SAP ECC can take months or even years, depending on the scope of the project. It’s not something you can just flip a switch and have it working overnight.
-
Change Management: Implementing SAP ECC often requires significant changes to your business processes. This can be challenging for employees who are used to doing things a certain way.
-
Integration: Integrating SAP ECC with other systems can be complex and require specialized expertise.
But don’t let these challenges scare you off. With careful planning, proper training, and the right implementation partner, you can overcome these obstacles and reap the benefits of SAP ECC.
Tips for a Successful SAP ECC Implementation
So, you’ve decided that SAP ECC is right for your business. Congratulations! But now comes the hard part: implementation. Here are a few tips to help you succeed:
-
Start with a Clear Vision: Define your goals and objectives for the implementation. What do you want to achieve with SAP ECC? What problems are you trying to solve?
-
Assemble a Strong Team: Put together a team of experienced professionals who have the knowledge and skills to guide the implementation. This should include both internal employees and external consultants.
-
Develop a Detailed Plan: Create a comprehensive implementation plan that outlines the scope of the project, timelines, resources, and responsibilities.
-
Prioritize Data Migration: Data is the lifeblood of your business. Make sure you have a plan for migrating your existing data to SAP ECC accurately and efficiently.
-
Provide Thorough Training: Train your employees on how to use the system effectively. This will help them adapt to the new processes and maximize the benefits of SAP ECC.
-
Test, Test, Test: Before going live, thoroughly test the system to identify and fix any issues.
-
Don’t Forget Change Management: Communicate with your employees throughout the implementation process and address their concerns. Help them understand the benefits of the new system and how it will make their jobs easier.
-
Monitor and Optimize: Once you’re live, continuously monitor the system’s performance and identify areas for improvement.
The Future of SAP and ERP Systems
The world of ERP is constantly evolving. Cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things are all having a major impact on how businesses manage their operations. SAP is investing heavily in these technologies to deliver even more value to its customers.
Expect to see more and more SAP solutions move to the cloud, offering greater flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. AI will play an increasingly important role in automating tasks, improving decision-making, and personalizing the user experience. And the IoT will enable businesses to connect their physical assets to their ERP systems, providing real-time visibility into their operations. Due to SAP ending support for ECC, every company currently using SAP ECC will eventually have to move to S/4HANA or another ERP system.
Final Thoughts
SAP ECC has been a cornerstone of enterprise resource planning for years, but the future is clearly heading towards S/4HANA and cloud-based solutions. Understanding the fundamentals of SAP ECC is still valuable, as it provides a solid foundation for navigating the ever-changing landscape of ERP. Whether you’re a seasoned SAP professional or just starting out, it’s an exciting time to be involved in this field. Keep learning, keep exploring, and keep pushing the boundaries of what’s possible.
And remember that bakery example? All those processes? Well, they all need to be secured, right? And that’s where Pathlock comes in.
Securing Your SAP Environment with Appsian
As you embrace the power of SAP, you’ll also want to make sure you’re protecting it from risks. Appsian offers a comprehensive Cloud Software platform that helps you manage access governance and cybersecurity across your SAP and other business-critical applications. It’s designed to simplify audit and compliance, prevent data breaches, and reduce the risk of fraud. Appsian integrates seamlessly with your existing SAP environment, providing real-time visibility and control over user access, segregation of duties, and sensitive data.
Ready to see how Appsian can help you secure your SAP environment? Get a demo today! It’s a smart move towards a more secure and efficient future.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Appsian Enhances SAP GRC with Cross-Application SoD & Risk Management
What is SAP GRC?
SAP Governance, Risk, and Compliance (SAP GRC) is a set of SAP solutions that enable organizations to meet data security and compliance standards. These solutions also provide control mechanisms to manage and mitigate risk. SAP GRC consists of four major components and multiple modules that manage risks, controls, identities, cyberthreats, and international trade across the SAP ecosystem.
What are the Components of SAP GRC?
SAP GRC features four major components that unify enterprise risk and control activities on a single technology platform. Each component has a set of modules that serve a specific function. As a whole, SAP GRC solutions give decision-makers the insights needed to adjust strategies and objectives while enabling them to predict, detect, and respond to business threats and opportunities. The four core components include:
Enterprise Risk and Compliance
Modules: SAP Risk Management, SAP Process Control, SAP Financial Compliance Management, SAP Business Integrity Screening
Cybersecurity, Data Protection, and Privacy
Modules: SAP Enterprise Threat Detection, SAP Privacy Governance, SAP Data Custodian
Identity and Access Governance
Modules: SAP Access Control, SAP Cloud Identity Access Governance, SAP Identity Management, SAP Single Sign-On
International Trade Management
Modules: SAP Watch List Screening, SAP Global Trade Services
Enhancing Your SAP GRC Capabilities with Appsian
While SAP GRC is a good tool to implement GRC across your SAP systems, it has certain noteworthy limitations. Appsian’s GRC solution goes beyond the SAP ecosystem to provide unprecedented visibility of real-time authorization usage and implement fine-grained, adaptive controls across applications. This significantly improves security while reducing fraud, risk, and exposure to sensitive data at an enterprise level. In addition, Appsian can be deployed as a stand-alone solution or combined with your existing SAP GRC solution to enhance security and risk management.
Here are some of the ways Appsian can enhance your GRC capabilities.
Cross Application Connectivity
Most companies utilize multiple ERP platforms for their business operations. Though SAP GRC offers a range of modules and controls, it can be deployed only within other SAP applications. Appsian integrates with several business applications like Salesforce, Workday, Oracle, Microsoft, Infor, or industry-related applications without any third-party connectors. Appsian GRC seamlessly connects all your applications to a centralized system for unified GRC management.
Attribute-Based Access Controls
Many ERP applications, including SAP, offer only role-based access controls. While role-based access works well when the user connects through a secure network like the office, today’s workplace demands a more adaptive approach to access controls. Appsian utilizes contextual attributes like location, device, time, IP address, and more to determine access risk and allows security teams to implement policies based on these attributes. Additionally, unlike role-based authorizations that are granted at access, Appsian’s fine-grained controls go beyond the point of access down to the data field and transaction level to deliver layered security, enhanced compliance, and improved user governance across multiple applications using a single control platform.
Authorization Management
As new users are added, and existing users are granted more roles, it becomes increasingly difficult to track and manage user authorizations, especially when dealing with multiple ERP applications. The result is user overprovisioning that creates greater data exposure, SoD conflicts, and overall risk. Appsian tracks authorization usage to recommend the elimination of unused and underused authorizations and access rights, making the monitored applications safer and simpler.
User Monitoring
While SAP GRC allows you to monitor and manage identities and control who has access to information, it provides little insight into what authorized users are doing within the applications. Appsian enables you to know what your users are doing, what tables they are accessing, what changes are being made, and by whom. It provides a detailed report of user activity data and allows you to set up alerts when sensitive information or tables are accessed.
Identification of Irregularities
The ability to continuously monitor user activity across applications also allows Appsian to track each user to identify and compare authorizations within each department or business unit for any discrepancies. The solution sends a notification to the management team of any suspicious activity that needs further investigation. However, the lack of user monitoring in SAP GRC means that such irregularities go unnoticed.
Impact on Licensing Costs
It is well-known that SAP licenses do not come cheap. Additionally, SAP does not provide a clear view of user roles and licenses. This makes it difficult to understand the cost impact of granting new roles/licenses to users. Appsian’s GRC solution considers licensing costs when recommending the best role to grant users by attaching costs to authorized roles and suggesting a less costly role when available. This allows you to manage your SAP license costs better and avoid overprovisioning.
Appsian’s enhanced approach overcomes the limitations of traditional SAP GRC, enabling you to manage identities, access, authorizations, and risk across multiple ERP platforms. Schedule a demo with our ERP GRC specialists to learn more about our GRC capabilities.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How To Handle Expiring SAP User Role Assignments
There are many reasons why SAP customers need to provide temporary access to their applications. These include short-term contractors or consultants, backup access when an employee is on vacation or suffering a long-term illness or disability, and emergency access scenarios. Regardless of the reason, organizations often encounter a common challenge: temporary SAP user role assignments expire without alerting the users. This lack of notification could potentially leave users locked out of applications or without the ability to perform their assigned tasks.
One of our clients, a leading multinational company based in Sweden, brought this to our attention and asked us to create an automated process for handling these expiring temporary SAP user roles.
The Challenges of Managing Expiring SAP User Roles with a Manual Process
Having to manually search through hundreds of thousands of profiles to find which roles have expired is time-consuming. In addition, it may lead to human errors and frustrated users. An automated role management solution effectively checks if a user still needs a particular role and automatically extends a required role or removes any unused roles.
For example, let’s consider an SAP user, Sarah. She has a role assignment expiring for her user ID in three days. She would not know that her ID expired until she logs in to the system on the third day and receives an error message. Next, Sarah must contact the helpdesk or her manager to request an extension. The approval process for this request could take 1-2 business days or more. The entire workflow would entail a series of manual processes and approvals. This would affect her ability to perform her daily tasks and negatively impact her productivity.
Use Automation to Prevent Temporary Roles from Expiring
Working with our client, Appsian Security created a process that automates how temporary SAP user role assignments are handled. It helps keep the users in control and accountable for their roles and authorizations while allowing them to extend roles if needed. In addition, the process ensures that users are not left without their roles, allowing them to continue performing their regular tasks. This helps improve the user experience and productivity for our SAP customers.
In a nutshell, Appsian’s automated role management and authorization solution helps SAP customers with the following:
- Fewer inquiries: Automating the SAP user role management and authorization process leads to fewer requests placed with the IT department and improves the turnaround time.
- Limited glitches: Users would no longer lose the ability to perform their usual duties due to the sudden expiry of temporary role assignments.
- Time management: Authorization managers no longer need to waste their time manually adding or removing roles.
- Automation: IT teams are relieved of manual approvals and processes.
- Resource management: Teams freed from time-consuming manual processes are better utilized for other functions.
- Documentation: All processes are now documented, making the workflow more efficient and audit-ready.
- Better user experience: With minimal glitches and less time spent on manual processes, there is a significant improvement in user experience.
Contact us today for a full demonstration of how to automate role management and authorizations in your SAP applications.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
Appsian How-To: Enforce Transaction Level Policy Controls in SAP
The typical business application’s role-based access control (RBAC) security model provides poor dynamic transaction level policy control enforcement. In this video demonstration, you’ll see how to enforce transaction level controls in SAP using attribute-based access controls (ABAC). You’ll also see how Appsian Security’s analytics platform, Appsian360, allows you to monitor user behavior around those transactions and spot deviations from normal behavior.
Gartner recommends transitioning from the static RBAC security to Adaptive Security found in an Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) security model. ABAC allows you to set controls based on policies and enforce that control at the transactional level or at the field level. The good thing about this is we can enforce transaction level controls in one place, and we can make it work across the different transactions. In other words, it’s a one-to-many level of control.
You can then use Appsian360 to monitor the most often run transactions, where they are most frequently run from, and the active status of these transactions.
What is Adaptive Security?
Adaptive security is an approach to managing security that analyzes behaviors and events to protect against and adapt to threats before they happen. With an adaptive security architecture, an organization can continuously assess risk and control effectiveness monitoring and automatically provide proportional enforcement that can be dialed up or down to fit its need.
- Adaptive Security is configured using combinations of contextual attributes, to enforce policy requirements into the access controls, thus automating policy enforcement.
- Adaptive Security constantly monitors and analyzes detailed user behaviors at the transaction and data level to detect threats, and then adapts the security controls to respond to threat with a mitigation action.
- The specific policy requirements configured into the access controls become the “key risk indictors” that Appsian360 can monitor to detect and report anomalies and threats.
Contact us today for a full demonstration on how to implement policy controls at the transaction level in your ERP applications.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
SAP Access Management: Automating and Centralizing the Identity Lifecycle
If you do an internet search for the most common cause of data breaches, you’re going to get a variety of answers: ransomware, phishing attacks, stolen credentials, insider activity, etc. While these types of cyberattacks lead to data breaches, there is one simple truth ERP customers can never overlook: data breaches are caused by unauthorized access. Of course, not all unauthorized access is malicious. It can also be accidental due to poor access management (also called identity lifecycle management).
Clearly, the best practice is using the principle of least privilege to grant access to the applications, transactions, and data that a person needs to carry out their jobs. While data security and privacy are the primary elements of a successful access management process, the overall identity lifecycle management process should be automated, centralized, and provide IT teams and business units with audit-ready information. This information is critical for providing reasonable assurances that their SAP access management process is compliant and operating effectively.
Poor Access Management Exposes SAP Data to Risk
The process of SAP access management shouldn’t exist in a vacuum or a silo. Unfortunately, many organizations struggle with manual and decentralized identity lifecycle management. This leads to a variety of situations where unauthorized access leaves valuable ERP data exposed to risk:
- Unused new accounts with default passwords
- Employees collect new authorizations as they move around the business without removing unnecessary ones
- New employee authorizations causing SoD issues and sensitive access issues
- Employees leaving the company while their user IDs remain valid
- And many more
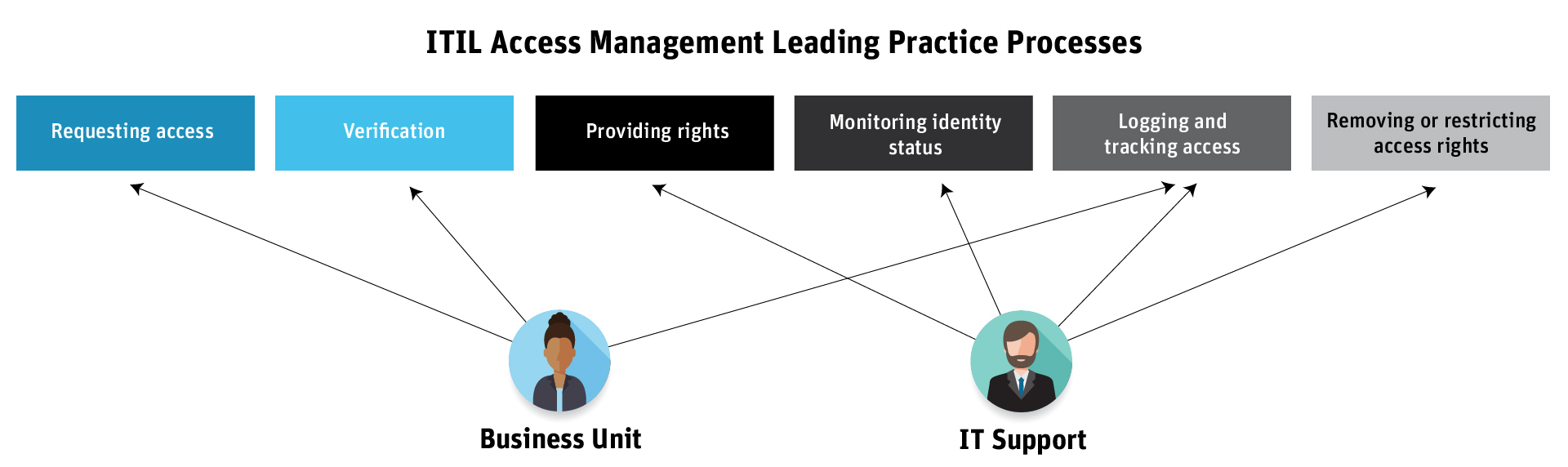
The identity lifecycle requires a process for controlling user access to critical information within an organization. The IT Infrastructure Library (ITIL) has a framework of best practices for access management: Requesting access, verification, providing rights, monitoring identity status, logging and tracking access, and removing or restricting access rights. But one department isn’t more responsible for the access management process than another, as outlined in this diagram:
While business leaders are the first line of defense and are responsible for owning and managing their risks, those business unit leaders and the IT departments are responsible for assigning and monitoring user privileges in ERP systems. Unfortunately, existing access management processes are manual, siloed, and error-prone. For instance, HR might request access by emailing IT or using a self-service portal to create a request. IT might use a provisioning solution that’s included out-of-the-box with their ERP system. But this approach is still mostly manual and exists in siloes, requiring one unit to rely on each other for updates.
This less-than-optimal approach leaves organizations exposed to security and compliance issues. Increasingly, organizations are under regulatory pressure to prove they are protecting access to corporate resources. As a result, organizations can no longer rely on manual and error-prone processes to assign and track user privileges.
Audit-Ready Access Management
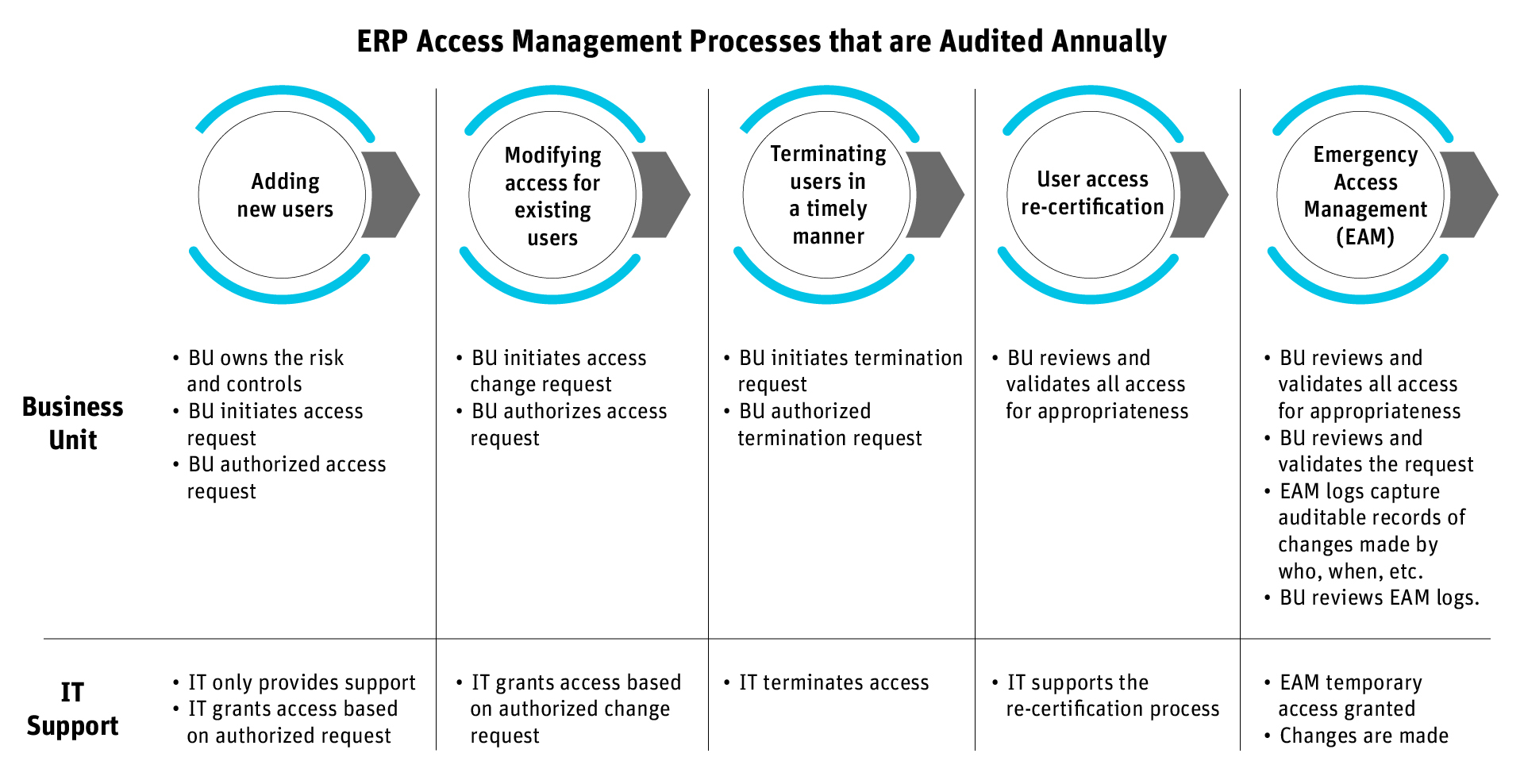
A poorly managed identity lifecycle process not only leads to security gaps but also visibility and compliance gaps.
As you can see from this illustration, all departments involved with access management will be audited to prove that their internal processes’ operating effectiveness sufficiently manages access risks, data security risks, and data privacy risks.
What’s missing for many organizations is an access management solution that centralizes and automates these tasks and enables granular access control and auditing of this process.
Automating and Centralizing Access Management with the Appsian Security Platform
Taking control of SAP access management from the start is key to enforcing data security, maintaining internal and external compliance, and adhering to various regulations. With ProfileTailor GRC from Appsian Security, you can easily organize, understand, and control the identity lifecycle process across your ERP landscape. Enabled by artificial intelligence, machine learning, and predictive analytics, it continuously identifies potential risks and provides optimized suggestions to streamline access management, including:
- Recommending the best alternatives when activities need to be removed from a user.
- Recommending the optimal segregation of roles to sub-roles according to business needs and actual usage. It automatically locks and removes the old authorization role from users who had it before the split.
- Solving SoD violations by replacing a user’s current roles without losing access to the activities actually needed.
- Choosing the optimal authorization role to grant users that enables them to perform additional activities without violating SoD policies.
Contact the SAP experts at Appsian Security for a demonstration on how you can prevent unauthorized user access at the transaction and master data level.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
3 Critical SAP Risks to Prioritize In A Dynamic Business Environment
SAP applications are the backbone of business operations across the world. They improve efficiency and help your business grow. But are they equipped to protect your business and data? The risk landscape is constantly evolving, with users working remotely and using personal devices to access enterprise SAP applications.
Since SAP is a critical business application used to access sensitive data and execute high-value transactions by thousands of employees across multiple locations, an effective SAP risk management capability should be an essential element of your security and compliance strategy. Here are the three critical SAP risks that, when not properly mitigated, can lead to a material level control weakness during your external audit that you need to prioritize:
Transaction Risks
Significant risks can occur at the business transaction level if effective controls are not enabled within your SAP applications to prevent or detect these risks. There are multiple scenarios where a lack of transaction-level controls could enhance risk.
- Duplicate payments may occur because SAP may not be properly configured to detect the unique ID numbers associated with individual payments to prevent a duplicate payment from being created and approved.
- Excessive payments amounts can occur when the payment amount entered exceeded the actual amount required, and no independent review is required to verify the accuracy and completeness of the data input amount before the payment is finalized.
- Fraudulent payments can occur when segregation of duty issues exist, enabling the user to create and approve a fake vendor and then be able to create and approve payment to that vendor.
Without the necessary controls, these transactions could lead to misuse of finances, compliance failures, and fraudulent activities. Such risks can be mitigated by implementing security solutions that allow you to define fine-grained rules and policies that can act as checkpoints for even authorized users. Furthermore, consider implementing layers of security and controls to enhance your ability to detect, prevent, and respond to anomalies and threats at the segregation of duty, transaction, and master data level.
Data Integrity Risks
Data integrity is the assurance of data accuracy and consistency over its entire life-cycle. Data integrity risk is when data stored and processed by IT systems are incomplete, inaccurate, or inconsistent across different IT systems. It is a result of weak or absent IT controls that can verify the accuracy and completeness of data inputs and appropriately restrict access to view, change, or extract the data.
For example, an unauthorized change to financial data stored in SAP can negatively impact the accuracy and completeness of the organization’s financial reports, which is defined as a material level control weakness by external audits. Material level control weaknesses are the worst control deficiency, which the organization must publicly report during the period of occurrence, and can negatively impact the confidence of current and potential investors.
Managing data integrity requires implementing controls that can minimize exposure of sensitive data with dynamic data masking and logging of user activity so that any change to data can be monitored and tracked. Furthermore, consider implementing layers of security and controls to enhance your ability to detect, prevent, and respond to anomalies and to threats at the segregation of duty, transaction, and master data level.
Security Risks
Security risk includes the risk that access to your SAP applications is not appropriately restricted. Native SAP security features provide role-based static access controls that allow users to have unrestricted access based solely on roles and authorizations aligned with those roles. However, the evolving business landscape requires users to access systems from their homes, personal devices, and public Wi-Fi, significantly increasing security risk.
Access has become dynamic, and trust can no longer be implicit, making context-aware access control a necessity for the modern enterprise. For example, access from a foreign country, access to sensitive data beyond business hours, or access from an unknown device or location are potentially risky for any business.
If your SAP access controls do not take context into consideration, your overall risk significantly increases. In simpler terms, the greater awareness of context your system has, the greater your ability to mitigate and manage risk. Furthermore, consider implementing layers of security and controls to enhance your ability to detect, prevent, and respond to anomalies and to threats at the segregation of duty, transaction, and master data level.
SAP Risk Management with Appsian
The Appsian Security Platform enhances SAP’s existing Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) with Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC), allowing you to deploy data-centric security policies that leverage the context of access and enable risk management across your SAP ecosystem. Additionally, it enables you to implement layers of security and controls to enhance your ability to detect, prevent, and respond to anomalies and threats at the segregation of duty, transaction, and master data level.
Click here to get a better understanding of how Appsian can help manage your SAP risk.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
Solving Complex Security Challenges with Dynamic SAP Data Masking
It’s been a period of unprecedented change and adaptation for organizations of all sizes and in every industry over the past 18 months. During this time, I’ve had the opportunity to speak with many of our SAP customers about how they are managing their business risks and protecting their sensitive data. While the topics vary, I’ve noticed a recurring theme: there is a growing—and urgent—interest in using SAP dynamic data masking to strengthen data protection and enforce governance and compliance policies.
But what exactly do we mean by SAP “dynamic” data masking, and what are the best practices for using it to manage business risks and increase data security?
Dynamic Data Masking in SAP Starts with Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC)
Data masking is used to protect various types of sensitive and personal data stored in ERP applications, including intellectual property, personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, such as credit card, bank account information, and more. As traditional security perimeters dissolve and compliance requirements increase, protecting your ERP data is of growing importance. This is where dynamic data masking shines. Focused on protecting data at the UI-level in production systems, dynamic data masking can significantly reduce your risk exposure.
A Quick Clarifier: Often, data masking is used in non-production environments to protect ERP data copied from production. This technique is also known as data obfuscation, data scrambling, or data anonymization – and modifies the data itself – meaning it does not work for production systems. Dynamic data masking obfuscates information at the presentation layer (UI-level) without affecting the underlying data (at the database level).
Before dynamic data masking, traditional data masking policies used a static, role-based approach. For example, you include the role(s) and the field(s) in your rules – and a mask is always applied in all circumstances. While it minimized exposure, the static nature limited adoption as it would create barriers to data, and policies would have to be continually updated as users changed roles.
Dynamic data masking extends this policy logic by incorporating attribute-based access controls (ABAC), allowing flexible and wide-reaching rules to be created that incorporate identifiers such as role and other user, data, and access attributes. For example, user’s residency or security clearance, org code, IP address, location, and much more.
Static data masking versus dynamic data masking seems cut and dry. However, my conversations with SAP customers revealed two distinct approaches to using dynamic data masking: One focused on user attributes, and the other focused on the dynamic attributes of access and data itself. While the former allows simple, wide-reaching data masking that addresses functional risk, the latter enables a contextual, risk-based approach that truly balances data security with the needs of the business to access data.
Data Masking Approach #1: Wide-Reaching Policies Based on User Attributes
Many organizations start their data masking journey by analyzing how necessary it is for specific users to see specific data. Focused on functional risk, this approach aligns to least privilege and sets out to mask data that is unnecessary for a user’s job. For example, does a customer service rep need to see the full bank account info on an order? In most cases, no. Or should an HR manager be able to view the PII in a user’s profile from another business unit they are not responsible for? Certainly not.
Using dynamic data masking in these scenarios can deliver wide-reaching policies that incorporate user attributes such as role, business unit, org code, or country of residency. The ABAC technology allows data masking to be enforced “dynamically” when any activity that matches the defined conditions is present. (Meaning there is no need to make changes when users change roles, new users are created, etc.)
This approach is superior compared to the legacy approach that relies on static, role-based policies. Data exposure can quickly be minimized, and from a lifecycle management perspective, ownership is much simpler. However, data is still masked at all times for users, which means the practical scope of usage is still limited.
Data Masking Approach #2: Risk-Based Policies Based on Access Attributes
I’ve recently noticed a shift in thinking from policies based on user attributes towards those based on access attributes. Organizations might be realizing, thanks to the growing number of data privacy regulations and enforcement fines, that their data is now a liability, and they need to implement more risk-based masking policies based more on access attributes than user attributes.
Now an organization can leverage context-aware access controls to mask data in high-risk scenarios and show data in trusted scenarios. For example:
- Masking unpublished financial data from unknown IP addresses/locations
- Masking sensitive business data outside regular working hours
- Masking data for emergency access sessions
A recent use case for this approach to SAP dynamic data masking is on display at a Canadian rail company that needed to provide secure access to sensitive data to a hybrid workforce while also allowing access to self-service SAP modules on mobile devices for their remote workers traveling from city to city and connecting from wherever they have a Wi-Fi connection. They were able to enforce risk-based data masking policies based on access attributes such as location, IP address, time, data sensitivity, and more.
Protecting Data with SAP Dynamic Data Masking Solution
The more I speak with our SAP customers, the more I realize the different “definitions” they have about dynamic data masking. The more accurate definition is that SAP dynamic data masking uses risk-based policies based on access attributes. Without ABAC, companies must enable data masking with extensive customization, resulting in an unscalable ad-hoc solution.
Fortunately, the Appsian Security Platform’s (ASP) dynamic data masking leverages ABAC capabilities to provide fine-grained control over which sensitive data fields can be masked for any specified user in the context of any situation.
I invite you to contact the SAP experts at Appsian to learn how for yourself how we can improve SAP data security and reduce compliance risk with a fully dynamic data masking solution.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
Data Loss Prevention: 7 Best Practices for SAP Security
A constantly evolving threat landscape and compliance environment with inconsistent standards have made data loss prevention (DLP) a vital component of an organization’s SAP data security strategy. The global cost of data breaches hit a record-high in 2021 ($4.2 million per incident), highlighting the importance of a robust DLP strategy to protect organizations from financial, legal, and reputational damages.
What Is Data Loss Prevention?
Data Loss Prevention is the practice of identifying and preventing data breaches, exfiltration, or unwanted loss or destruction of sensitive data. Businesses use DLP solutions for SAP and PeopleSoft applications mainly to:
- Secure Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
- Comply with data security and privacy regulations
- Protect intellectual property critical to the organization
- Prevent unauthorized transfer of data outside the organization
Seven Data Loss Prevention Best Practices
For any DLP strategy, you need to understand which organizational data to secure, where that data resides, who has access to that data (and when), and how the data should be used. Unfortunately, data loss is difficult to spot because data routinely moves in and out of an enterprise and closely resembles normal traffic. Let’s take a look at a list of data loss prevention best practices that have helped our customers achieve their data security goals and meet compliance standards.
- Configure Dynamic Data Loss Prevention Policies
Preventing unauthorized exposure of sensitive information and protecting against insider data leakage begins by configuring contextual, attribute-based DLP policies that restrict transactions based on user and data attributes. Unfortunately, traditional role-based access controls (RBAC) can’t completely safeguard data in dynamic environments as static roles fail to leverage contextual attributes such as time of the day, geolocations, IP address, transaction type, etc.
- Establish Clearly Defined Rulesets for Segregation of Duties
Establishing a clearly defined ruleset for segregation of duties that divides business processes between multiple users helps limit the risk of fraud and error while ensuring that a user’s access privileges do not conflict or violate business policies.
- Deploy Policy-Based Data Masking and Redaction
Companies can enable dynamic data masking to reduce unnecessary exposure of sensitive information while allowing employees to do their jobs. For example, masking specific fields on a page an employee is accessing. Or using click-to-view masking to unmask data or require an MFA challenge before data is revealed to log access to a particular field. And don’t forget to protect non-production environments where dynamic data masking ensures development or testing teams can only access the data they need and nothing more.
- Continuously Monitor Data Access And Usage
Monitoring user behavior around data access and usage in real-time at a granular level provides visibility into how users interact with sensitive data, triggering security event alerts for high-risk access and abnormal activity at the field level. (Native application logging capabilities cannot tell the difference between malicious user activity and normal usage.)
- Increase The Levels Of Access Control & Monitoring for High-Privilege Users
Because privileged user accounts are magnets for hackers, companies should isolate activity and access data by these accounts to ensure integrity and alignment with current business policies. For example, an employee from the HR department needs access to payroll information to do their job, but do they need that access outside of office hours or from an unknown IP address?
- Closely Monitor Report and Query Downloads
Monitor instances of query running and download attempts, ensuring that sensitive queries are not being downloaded onto unauthorized devices, from suspicious locations, or outside business hours.
- Leverage DLP Solutions to Automate As Much As Possible
For all the features and value ERP systems provide, they lack the functionality to provide a dynamic, automated data loss prevention solution. Automating DLP processes across the organization allows you to enforce dynamic policies to identify and protect data before it exits the organization. In addition, automating compliance audits allows you to constantly monitor data access and usage and alert security teams to abnormal activities.
How Appsian Security Helps Enable Your SAP Data Loss Prevention Strategy
Whether careless or malicious, employee, partner, or contractor, it can be difficult to tell the difference between a user’s regular activity and activity intent on causing harm or theft. The Appsian Security Platform (ASP) helps SAP customers deploy these data loss prevention best practices, and many more, to prevent unauthorized exposure and exfiltration of sensitive data, PII, and intellectual property.
By configuring dynamic access controls, you can uniformly enforce policies that restrict transactions based on user and data attributes. In addition, you can deploy policy-based data masking that help you comply with data security and privacy regulations by reducing the exposure of high-risk data.
Contact us today for a demonstration and see for yourself how Appsian Security can help with your data loss prevention strategy.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
SAP Access Controls: How RBAC & ABAC Work Together
To ensure employees remain productive in a dynamic and hybrid work environment, organizations use SAP access controls to allow their workers remote and secure access to ERP data, transactions, and self-service modules. Unfortunately, the existing SAP role-based access controls (RBAC) have reached their limitations in a dynamic workplace because static roles do not leverage contextual attributes.
Understanding SAP Access Control Using RBAC
Functionally, role-based access control (RBAC) is a policy-neutral approach to granting (or restricting) SAP access based on the roles of individual users in the company. Since RBAC was intended for on-premises data access from behind a corporate firewall, it creates a very strict, static set of permissions. You either have access or you don’t.
RBAC has always provided a strong foundation for setting SAP access controls. However, the way people are interacting with data resources is constantly evolving and RBAC is struggling to keep up.
Enhancing RBAC by Using Attribute-Based Controls in SAP
Organizations are looking for more flexible and secure ways to grant users access to only the information and resources they need to perform a particular task. This dynamic approach to SAP access controls enhances RBAC by considering different “attributes,” enabling security policies to be dynamic and “data-centric” and leveraging a user’s context of access to determine access to data. By incorporating these attribute-based access controls (ABAC), organizations can control user access more precisely, and better balance policy and security requirements.
The more attributes you can incorporate, the more precisely you can define what, how, and when a user or group of users can access data. Unlike RBAC, ABAC allows you to use contextual information such as project ID, company code, IP address, location, device type, and more to authorize access.
The RBAC + ABAC Hybrid SAP Access Control Model
Appsian Security extends and enhances existing SAP access controls by combining RBAC security capabilities with attribute-based policies. Starting with RBAC, organizations set the foundation of their access policies. ABAC begins the moment users start to access data and transactions and considers the context of access (who, what, where, when, and how) before allowing a user to access transactions or data.
The key benefits of the RBAC + ABAC hybrid model from Appsian Security include:
- Reducing Attack Surface
Organizations can reduce their amount of accepted risk by applying granular business policies and contextual access controls to strengthen data-level and transaction-level security. - Dynamic Data Masking
You can dynamically enforce data masking or outright restriction policies to any field in SAP when using real-time contextual policies that balance security and usability. - Reinforcing SoD Policy Violations
Adding ABAC to RBAC allows you to apply preventive controls in segregation of duties (SoD) exception scenarios. By doing so, you can prevent SoD violations while still allowing the flexibility of conflicting roles to be assigned (when necessary) and reinforces role-based policy to mitigate over-provisioning.
Without a solution like Appsian Security, the closest organizations can come to granting policy-based access to SAP is through customization or adding role derivations to a user for each attribute. Both options are costly and add complexity and overhead to role management in the long run.
Contact us today and schedule a demo to see how Appsian can help you enforce SAP access controls beyond the standard RBAC model.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives