Why Automation is Key to Resolving SoD Conflicts in SAP
Companies using SAP typically have some type of structured governance, risk, and compliance (GRC) strategy to manage their overall governance and enterprise risk management and meet compliance requirements. An essential component of any GRC strategy is detecting and resolving SAP segregation of duties (SoD) conflicts.
SoD weighs heavily on financial management and reporting, especially for public companies or those receiving government funds. When unresolved SOD conflicts appear on audit reports, a company’s compliance with the Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX) and data privacy regulations like GDPR are negatively impacted.
Spreadsheets: The Traditional Approach to Managing Segregation of Duties
For a long time, companies have relied on spreadsheets to track and maintain roles and authorizations granted to employees. While spreadsheets are great to get started on your compliance program, they can create several hurdles as your organization grows in size and complexity.
- Human Error: No matter how meticulous, humans are prone to making errors, especially when dealing with thousands of rows across multiple sheets and files. Every new change can trigger a cascade of changes which is hard to keep track of manually.
- Low Visibility: In most cases, it’s more than just one person working on the spreadsheet with no visibility into who is editing what and where. With multiple teams/members making changes, the probability of error also increases.
- Reporting Delays: Collating, validating, and analyzing data that is spread across various tabs and files requires a significant amount of man-hours. This results in reporting delays and after-the-fact detection of SoD conflicts.
- Lack of Audit Trails: Simply put, Excel sheets cannot maintain an audit trail. Even if you can track changes, getting into each version of the file to view changes is a long and laborious process.
- Limited Insights: Spreadsheets are static and do not have the ability to cross-reference data to provide actionable insights. Also, manually sifting through large volumes of data makes it difficult to detect behaviors that impact risk.
The reasons mentioned above make it abundantly clear that the spreadsheet method of tracking and resolving SoD violations is slow, inefficient, and error-prone. With regulatory authorities imposing compliance mandates and hefty fines on companies that fail to meet audit requirements, there is an immediate need to update your approach to GRC with tools that are equipped for the job.
Segregation of Duties Conflicts Are Not Static
An increasing number of companies who use SAP are realizing that segregation of duties conflicts are a significant cause of audit failures. This is mainly because SAP authorizations are not static, and neither are SoD violations. As employee roles and duties change over time, it becomes difficult to keep track of authorizations and SoD rules that govern the limits of each role. For example, when a procurement team member who is authorized to approve new vendors retires, this role could be assigned to someone on the team who is authorized to issue purchase orders. This immediately creates a conflict of interest and results in an SoD violation.
In large organizations, such violations happen regularly, and without the tools to detect and resolve them immediately, an audit failure is inevitable. To address this challenge, companies deploy simulation solutions that allow them to see if granting an authorization could cause an SoD conflict. However, these results are generally ignored since most simulation tools do not offer options to resolve the conflict. The reality is that holding up authorizations can directly impact the operational efficiency of the business, which usually wins over compliance requirements in the short term.
Automation is the Key to Resolving SoD Conflicts
To be able to proactively detect and prevent SoD violations, organizations need to go beyond simulation and invest in solutions that can constantly monitor SAP roles and authorizations. In fact, solutions that can go one step further and offer options for resolution will allow administrators to quickly take action without creating further conflicts. Appsian Security ProfileTailor GRC was designed keeping in mind the challenges faced by companies who struggle with meeting compliance due to SoD conflicts. With real-time automated monitoring capabilities, ProfileTailor GRC enables you to immediately detect and resolve SoD violations within a matter of minutes.
Whether you have new employees needing authorizations, current employees changing positions or roles, or someone leaving the organization, ProfileTailor GRC will do the heavy lifting for you and provide you with an ongoing, fully automated, and integrated solution.
Download our white paper Quickly Resolve Segregation of Duties Conflicts to learn how automation can help enable GRC in your organization.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
You’re Spending Too Much on Your SAP Licenses. Here’s Why!
There is no denying that SAP applications make it easy for large organizations in almost every industry to streamline their business processes. However, that ease doesn’t include SAP software license management, which by all accounts, is considered one of the most complex compared to other ERP vendors. This complexity results in companies buying more licenses than they need or inefficient management of their existing SAP license types, which significantly impacts the overall costs. Here’s why you end up spending more than you should on your SAP licenses (and a tool that can help you save some money).
Vague SAP License Descriptions
SAP license descriptions are not airtight, and it is mainly left to you, the customer, to decide the type and number of licenses you need. SAP licenses can be broadly categorized into three types.
- Professional License: A named user with a Professional License can perform operational tasks and has administrative privileges that allow them to make changes to the system – usually assigned to employees who are heavy users.
- Limited Professional License: This license is ideal for employees who need to perform operational roles supported by the SAP software. It is a step down from the Professional License and is also cheaper.
- Employee License: With this license, users can perform tasks solely for their own use and not on behalf of anyone else. This license costs the least.
An SAP license is always associated with a user who is called a named user. The ‘name’ in this context is not an actual user name but a unique ID linked to a license. There can only be one license associated with a named user at any given time. However, a named user can have multiple user names to access different SAP systems.
This makes it increasingly complicated to assign the appropriate license type. For example, a single user could be using an ERP system for updating inventory, a second ERP system for monthly invoice approvals, and a third one for downloading reports. Which license would be applicable in such a case? Now imagine figuring out license types for thousands of employees accessing multiple systems.
Improper User Classification
User classification is a crucial exercise for SAP software license management that directly impacts your license cost and the recurring annual support fee. Most SAP customers classify their users with one of three parameters:
- Amount of Activity: The amount of activity performed by the user can be one way to classify the user. SAP measures activity by ‘Dialogue Steps,’ which is the number of screens and keystrokes used.
- Number of Different Activities: Users can also be classified based on the number of activities or the different applications they access on a regular basis.
- Type of Activity or Activity Group: The type of activity can be used as a yardstick for license purchases. Under this classification, users are grouped together based on the type of usage. This requires customers to assess the type of activities a user needs to perform and create groups.
Though this classification process appears straightforward, several gray areas occur when put into practice. For example, when classifying users by their amount of activity, a user could be using the corporate phone directory in the SAP system 1,000 times, but that does not mean he needs a Professional License. Or let’s say an employee is accessing multiple systems but only to generate reports. Under the second classification, this user would be eligible for a Limited Professional license, whereas an Employee License would most likely suffice since the user is only viewing and downloading data.
Classifying users as mentioned above makes logical sense, but large organizations need to invest a significant amount of time and resources for using these methods. Also, employee roles keep shifting, and usage may vary significantly over a given period. This makes classification difficult and impossible to maintain manually without errors.
That’s why SAP customers rely on automated tools like Appsian Security ProfileTailor LicenseAuditor to identify users based on their activities and distribute SAP licenses types accordingly. SAP software license management and auditing tools also help achieve compliance and manage SAP usage.
Knowledge Equals Savings
SAP licenses are a huge investment for any organization. Gaining a better understanding of your overall license status, usage, and spend not only helps you manage your current licenses but also allows you to negotiate a better deal. With SAP announcing the end of support for classic SAP applications like SAP ERP, SCM, SRM, CRM, and Business Suite by 2027, all customers will eventually have to migrate to SAP S/4HANA. By auditing your current SAP usage and forecasting future license requirements, you can ensure significant savings for your company as you go through with the migration.
Appsian Security ProfileTailor LicenceAuditor provides control over your SAP licensing by combining user inspection, user behavior-analysis methods, and best practices. The solution enables you to effectively utilize your licenses by offering a clear view of licensing possibilities for optimized models and savings of 50%-90% per classified license.
To learn more about SAP software license management, read our complete guide 5 Simple Ways to Reduce Your SAP License Spending.
Or contact us today for a ProfileTailor LicenceAuditor demonstration.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How SAP Customers Use Data Masking to Manage Global Business Risks
Here are two use cases that might sound familiar…
While organizations spend millions combatting external threats, for example, hacking, phishing, and ransomware, we at Appsian Security have found most data security use cases are focused on data governance across the enterprise. Simply put, what can someone access depending on where they’re located, what business unit they belong to, or even what time of day it is? Ensuring SAP data security policies are followed without over-restricting access or hurting productivity is a serious juggling act. Sadly, most organizations get it wrong. Fortunately, the solution can come down to a concept as simple as data masking – what, when, and how?
I had the opportunity to learn about two specific use cases (from Appsian customers) and how they used dynamic data masking to protect sensitive data—all without adding bottlenecks or complexity to their organization.
Transportation Company Use Case
While many industries struggled through the COVID-19 pandemic, a transportation and rail company based in Canada thrived. This was due to being a critical delivery component for many supply chains. The company had to transform its office-based workers into a flex-work model (hybrid workforce) and hire additional employees for fieldwork. The hybrid workers needed to continue their day-to-day managerial tasks, which contained sensitive information that the company was not comfortable exposing outside its secure corporate office. Securing access to this data was further complicated by remote workers traveling from city to city and logging into the self-service SAP modules on mobile devices from wherever they had a Wi-Fi connection.
The company turned to Appsian to enable a dynamic data masking solution by leveraging contextual access controls that determined which sensitive data fields and Tcodes employees could access based on attributes such as location, IP address, time, data sensitivity, and more.
International Consumer Packaged Goods Use Case
Where one company was dealing with multiple employee/user locations, an international consumer packaged goods company was dealing with multiple office locations around the world, each with its own installation of SAP. The company needed the means to protect sensitive personal data (stored in 1 of 5 unique SAP systems) while abiding by each location’s unique PII protection requirement (GDPR, PIPA, LGPD, etc.).
For this unique situation, the company needed a centralized data masking solution that could follow each location’s unique governance policies. All while being flexible enough to manage scenarios involving multiple locations and protecting sensitive data in production and non-production environments.
For example, a US-based employee could access the SAP system in the South American office. Yet, the dynamic policy could mask certain pieces of information or Tcodes because of the user’s nationality. The user’s location is from a legitimate IP address, but their nationality forbids them from accessing certain personal or sensitive information due to international regulations or company policies—even if that user can access that information in their own instance of SAP.
Protecting SAP Data with a Dynamic Data Masking Solution
The key to a successful dynamic data masking solution is the use of contextual access control policies (ABAC). ABAC allows companies to work in conjunction with existing roles-based controls (RBAC). Without it, neither one of these companies could successfully enable data masking without extensive customization, resulting in an unscalable ad-hoc solution.
Appsian Security Platform’s (ASP) dynamic data masking capabilities provide fine-grained control over which sensitive data fields can be masked for any specified user in the context of any situation. For example, ASP allowed both companies to:
- Centralize data masking enforcement throughout ECC and S/4HANA with a single ruleset.
- Deploy dynamic policies that account for risk based on the context of access, such as location, IP address, time, data sensitivity, and more.
- Protect sensitive data in production and non-production environments.
- Align SAP data masking controls with existing governance (corporate) policies.
- Mask sensitive PII based on the data subjects’ residency (country/nationality).
- Mask data fields in transactions (Tcodes) that are unnecessary for a role.
Contact the SAP experts at Appsian and see for yourself how ASP can improve SAP data security and reduce compliance risk with a fully dynamic data masking solution.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Appsian Reduces Risk in SAP Procurement Transactions
The sheer breadth and complexity of the procurement process can make maintaining effective internal controls difficult. Organizations must implement business process controls to ensure that employees only have access to SAP procurement transactions appropriate to their role and that the activity within these transactions falls in line with their established business policies. Having tightly aligned controls that prevent policy violations in the first place is critical to reducing the level of accepted risk in procurement business processes.
And this brings us to a key challenge in SAP procurement processes. Relying solely on SAP’s static role-based access controls (RBAC) has its limitations. Without the ability to consider factors beyond a user’s role and privileges, preventive controls may be impractical in certain scenarios, forcing reliance on detection and remediation in hindsight.
Enforce SAP Procurement Transaction Policies with Dynamic Access Controls
With the dynamic nature of procurement processes, extending your business process controls strategy to include data-centric and context-aware functionality can significantly reduce your risk exposure. Organizations using SAP ECC and SAP S/4HANA can strengthen policy enforcement by leveraging dynamic, attribute-based access controls (ABAC). Appsian extends SAP’s existing security model by enabling a fine-grain approach that shrinks the gap between business goals and security controls.
Let’s look at some specific use cases across SAP procurement transactions to demonstrate how Appsian can reduce SAP business process risks in today’s dynamic access environment.
Dynamically Controlling Purchase Order Creation
Purchase order creation is an important procurement transaction that should be controlled by an assigned threshold level and approval limits. Appsian allows you to easily manage risks associated with the purchase order process by extending dynamic controls into SAP based on factors such as PO dollar amount, location, time of day, and more.
For example, let’s look at a couple of employees:
| Employee | Total PO Threshold | Create POs when Remote? |
| George | Up to $5,000 | No |
| Gracie | Up to $25,000 | Yes. Between 8 am-5 pm |
You can allow George only to create POs that do not exceed $5,000 in value. He is also blocked from creating POs outside of the corporate network. For Gracie, she has the company’s approval to create POs up to $25,000 and can do it when working remotely as long as it is during normal business hours of 8:00 am to 5:00 pm.
Dynamically Enforce Segregation of Duties
During the procurement business process, there is a need to control the PO’s life cycle using Segregation of Duties (SoD). That means the same person can’t perform PO creation and GR (Goods Receipt) posting followed by IR (Invoice Receipt) posting.
Segregation of Duties policies that rely on static role-based rules can create unwanted business risk because they lack visibility into attributes that define actual conflicts of interest. This gap also carries over into SoD audit logs, resulting in excessive false positives when SoD exceptions have been made.
Appsian allows you to stop unauthorized user activity in real-time using a data-centric approach to enforce SoD controls. Our preventive SoD controls correlate user, data, and transaction attributes, along with identified SoD conflicts, to block conflicting transactions at runtime – even if they have the role-based privileges to perform the transaction.
This approach can add flexibility to procurement processes by allowing users with SoD exceptions to perform conflicting transactions that do not pose actual SoD violations while preventing those that do. The preventive SoD controls can also act as a safeguard to stop any SoD violations that may originate from privilege creep, such as a user changing roles without prompt deprovisioning of old privileges.
Limit Access to Sensitive Data by Masking with Conditions
Because the SAP procurement process touches different departments, it’s important to ensure that users do not have access to data or transactions outside of their roles and responsibilities. From protected PII to privileged financial information – this data carries risks that organizations must address.
Alas, there are no masking capabilities available out of the box in SAP. As a result, privileged users can access sensitive data fields even when access is unnecessary. This kind of unchecked data exposure leaves a massive threat surface that is vulnerable to exploitation and leakage.
Appsian’s Dynamic Data Masking provides SAP customers with fine-grained control over which sensitive data fields they can mask for specified users in the context of any situation. For example, you can decide to mask PII, account names, account numbers, etc., if access comes from an unmanaged device, unknown IP range, or outside typical working hours. Likewise, you can easily mask sensitive data in transactions where exposure is unnecessary for a certain role to do the task at hand.
Appsian: The Dynamic Approach to Reducing SAP Procurement Risks
Managing SAP procurement transactions exist in the overall category of reducing SAP business process risks. It’s a persistent challenge facing organizations of all sizes.
Contact the experts at Appsian today to learn how we can help you face this challenge head-on with our dynamic approach to managing your SAP business process controls.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Appsian Improves SAP Segregation of Duties Violations Management
From stopping fraud, theft, and errors to preventing SOX compliance violations, SAP Segregation of Duties (SoD) plays a lead role in minimizing business risk. Organizations must continuously iterate their internal controls to ensure their SoD strategy is effective; however, we all know this is easier said than done.
What are SoD Violations?
A Segregation of Duties or SoD violation occurs when a user has more control over a particular workflow than needed. For example, if a user can both approve new vendors and release purchase orders, it creates a conflict of interest that could, potentially, lead to fraud. The primary goal of implementing SoD is to, first, prevent users from gaining authorizations that create conflict and, second, to detect existing user authorizations that are in violation of organisational policies and/or compliance regulations.
Finite Resources & Manual Processes Can Only Address So Much
With existing capabilities, audit preparation and reporting are manually intensive processes that deliver an outdated snapshot of risk. Time and effort are wasted investigating immaterial events (i.e., false-positives, non-financial activity) because audit logs miss relevant details. Furthermore, manual analysis can be prone to errors, unscalable, and increasingly costly.
Due to resource-intensive audit processes, most organizations can only review a fraction of their SoD audit findings. This limited sample scope, typically between 3-8%, leaves the vast majority of risk unaddressed. While the sample may indicate control effectiveness, significant material risks may go undetected, and confidence will be curbed.
Leveraging Technology to Reduce Your SAP SoD Risk Exposure
Existing SAP SoD audit logs will show transaction activity but lack the data-level granularity to identify and filter out false-positive SoD violations. Manual investigation and correlation must be performed to do this – adding overhead, slowing the reporting process, and making it more difficult to prove compliance.
The bottleneck stems from technology and dictates unscalable processes. One approach to overcome this challenge is to adopt data-centric logging, which provides relevant details beyond roles and transactions – enabling customers to automate the majority of manual investigation and correlation efforts. From here, organizations can shift their valuable human resources towards remedial activities to further reduce SoD risks.
How Appsian Improves SAP Segregation of Duties Violations Management
Delivering data-centric logs paired with contextual information, Appsian360 provides visibility into SoD violations with far greater detail than what is possible with existing transaction-level audit logs. This additional information enables customers to eliminate false-positives automatically, view actual SoD violations, and prioritize events based on relevant details (e.g., dollar amount, time/location performed, etc.)
Leverage data-centric visibility to streamline SAP Segregation of Duties:
- Uncover 100% of SoD violations with data-centric continuous controls monitoring.
- Capture actionable details that would previously require manual investigation.
- Gain an always current view of SoD risks with continuous audit capabilities.
- Prioritize investigation & remediation activity by eliminating wasted effort on immaterial events.
- Simplify proving compliance with granular visibility and contextual information that is missing from existing audit logs.
- Get a Demo of Appsian360 and See for Yourself
As the burden of SAP SoD compliance grows, organizations must look towards technology to help automate tedious manual processes and strengthen internal controls. At Appsian, we’ve built our solutions with this need in mind, delivering a platform that enables SAP customers to do more with less. Contact us today for a demo, and let’s explore how we can help your organization streamline SAP segregation of duties.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
Implementing Dynamic SAP Data Masking in ECC & S/4HANA Using Appsian
2020 brought about a reckoning for organizations that were slow to adopt strong data privacy and data loss prevention strategies. As users went remote, the networks and devices used to access SAP financial data became a liability – and organizations were sent scrambling for solutions to their newfound dynamic access demands.
Why is data masking used?
Data masking is security measure used to shuffle, obscure, or encrypt data so that it cannot be accessed or deciphered without the requisite authorization. Masking of sensitive data like SSN, bank account information, healthcare records, and financial information in ERP systems like SAP allows enterprises to reduce unnecessary exposure of data while enhancing data security and reducing their overall risk. Data masking also helps private and public companies align with compliance regulations like GDPR, PCI DSS, Sarbanes Oxley, etc., which mandate the protection of all personal data from unauthorized access and theft.
Out-of-the-Box SAP Data Protection is Not Enough
In order to prevent data exfiltration and general over-exposure of enterprise data, the use of SAP data masking has grown in popularity. Unfortunately, customers have no out-of-the-box solutions for SAP data masking. In fact, the entire SAP security model hinges on static, role-based controls that offer little to actually protect the data inside the transactions that the access controls are designed to govern. In many cases, a user who has access to a transaction has access to a wide range of data within that transaction that simply isn’t necessary – providing opportunities for misuse.
To make matters more complicated, if an organization were to undergo a large-scale SAP data masking project, the sheer amount of custom development would prove to be a significant hurdle and nearly impossible to scale effectively.
Appsian Offers a Centralized, Scalable Alternative
To offer SAP ERP customers a scalable data masking solution, the Appsian Security Platform (ASP) features dynamic data masking capabilities that enable fine-grained control over which sensitive data fields customers can mask for any specified user and in the context of any situation. By implementing a full or partial mask to a data record, ASP minimizes the risk of a data breach and fulfills encryption and anonymization mandates imposed or implied by regulatory bodies.
Unlike most off-the-shelf masking solutions, Appsian uses a single ruleset to define and mask data across the entire application:
- Centralize SAP data masking enforcement with a single ruleset
- Deploy dynamic policies that account for risk contexts such as location, IP address, time, data sensitivity, and more
- Protect sensitive data in production and non-production environments
- Implement masking without requiring additional customizations to SAP
- Filter out sensitive data at the presentation layer, resulting in no additional maintenance requirements for updates
Why Appsian is the Essential Dynamic SAP Data Masking Solution
Simply put, when you are trying to protect data without overly-restricting access, then there is no alternative to leveraging a dynamic SAP data masking solution. Because the context of access plays such a critical role in defining risk, being able to apply full or partial masks based on context is the only real way to balance data protection and productivity.
In addition, Appsian uses a “one to many” approach for creating policy-based data masking rules. This enables customers to quickly scale SAP data masking without extensive development effort at implementation or reconfiguration efforts for policy updates.
Example Use Cases for Dynamic SAP Data Masking
- Mask PII of Customers in SAP CRM Based on their residency
GDPR Compliance – Ex: Mask PII Data if Customers’ Address is in the EU - Mask & Lock Bank Account Fields After Hours
Fraud & Theft – Ex: Insider Changing Data at Night Before Pay-Run - Obscure Data Fields in Transactions that are Unnecessary for a Role
Data Minimization – Ex: Customer Support Seeing Financial Spend, Pricing Info - Prevent Remote Access of Unpublished Financial Information
Risk Mitigation – Ex: Mask Data when Access Occurs After Hours or Remote
Get a Demo of Appsian’s Dynamic SAP Data Masking and See for Yourself!
As business processes become more complicated, your ability to protect data must evolve as well. Fortunately, Appsian offers the fastest, most cost-effective approach for SAP data masking. Contact us today and get a demo! And find out how you can be applying dynamic data masking rules within only 4-6 weeks!
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How IT Can Use ERP Data to Become a Hero to their Business Stakeholders
When business stakeholders come to you looking for answers, having visibility and context around ERP data access and usage gives you the actionable insight necessary to provide value.
As a leader of Enterprise Applications, customizing legacy ERP applications like PeopleSoft, SAP ECC, Oracle EBS, etc., to meet your business’ exact process specifications can leave you between a rock and a hard place. The more customized your ERP applications get, the more your business stakeholders love it, but the complexity around application support and maintenance also increases. That being said, accepting more complexity is just part of the job, because after all, your most important role (in the eyes of others) is providing timely and accurate resolution to inquiries or incidents from your business stakeholders.
You know the drill: members from various business units come to you requesting help for a particular incident or an anomaly they spotted. It’s up to your team to provide a resolution in a timely manner. And that’s where the trouble begins. Many incidents require hours, weeks, and even months to research and resolve. It’s hard to provide excellent customer service to the lines of business when your team is facing major obstacles to resolving incidents in a timely manner.
What if I told you there’s a way to enable your team to spend less time researching an issue (or no time at all) and produce faster results while providing better value for the various business leaders and their teams?
Three Major Obstacles to Timely ERP Incident Resolution
You’re the last person who wants to hear or say, “well, that’s just [insert ERP app name here].” But that’s one way you can sum up the limitations and obstacles your team will immediately encounter.
Here’s a simplified view of that process from the perspective of PeopleSoft. Somebody from a line of business will contact a member of your Sys Admin team and say, “Hey, this user’s account was updated (i.e., maybe they didn’t get their paycheck), or there was some sort of anomaly in the execution of a typical business transaction (i.e., vendor didn’t get paid, etc.). We don’t know what it is, and the functional user(s) say it wasn’t them. We’re not sure what happened. Can you guys look into this? That would be great.”
This incident kicks off your process flow to find a resolution. Then come the obstacles:
Obstacle 1: Legacy ERP Logs Can’t Tell You About Data Access
Experience says that most people who use an ERP application like PeopleSoft don’t know who’s doing what (specifically), who’s accessing what information, or most importantly – why. You probably first need to work out if this is something that the user did themselves or a hacker was able to gain access to the system – and also work out if this is an inside job or an external attack.
And while the logs can point you in the right direction, the legacy ERP logs are not designed to provide detailed information on who accessed what or even, in most cases, viewed something sensitive. This leads to major obstacle number two…
Obstacle 2: ERP Logs are Disparate and Not Correlated
ERP logs were designed for troubleshooting, not granular activity logging, which contributes to organizations and business units not knowing what their employees are doing inside the applications. When it’s time to go under the application hood and examine the native logs, another metaphor comes to mind: looking for a needle in the haystack. Here’s an example of all the native logs you might find in your instance of PeopleSoft:
- App Server
- PIA (Web Server)
- Database
- Process Scheduler
- Load Balancer
- Identity Provider (SAML, LDAP, ADFS)
- Host O/S Logs
- Firewall
Your organization likely has more than one of these servers where these logs reside. You might have four application servers, eight web servers, and so on. Now you’re looking at finding a needle in multiple haystacks. And that data is not correlated, so there is little relative context that can enable your investigation.
Here’s a nerdy example using the App Server and Web Server logs. On the Web Server, you cannot identify the person who logged in because you don’t know the OPRID. All you have are an IP address and a timestamp. You need to go to the App Server and review the OPRID, timestamp, and IP address on login or log out and attempt to correlate that information with similar information on the Web Server.
Obstacle 3: Log Data is Not Enriched with Any Context That Makes It Actionable
Once your team has collected data from the logs and assembled material from other sources, the final step is to interpret everything and make a best guess so an action item can be established. How actionable is having a collection of raw data such as IP addresses, user IDs, location of devices, completed transaction, etc., if you’re not able to place that data into a human context?
Let’s take the example of “Jim” and the incident involving him not receiving a paycheck. The raw ERP data shows that Jim’s credentials accessed pages containing personal information and bank account information several times over a period of time. Jim, the human, denies that he made any changes to the data on those pages, so the paycheck should have been routed to his usual bank account. Maybe you change Jim’s username and password and cut him another check. Was Jim trying to defraud the company and get an extra check, or was Jim’s account compromised in some way? Could a hacker have accessed Jim’s payroll data, changed the account number, received the funds, then changed the number back – getting away without a trace? Absolutely! It happens every day. If you cut Jim a new check, you fix Jim’s immediate problem, but do you understand what’s happening in your system?
Why Appsian360 Immediately Makes You a Hero to Your Organization
You’ve been waiting in suspense to know when IT becomes the hero – well, here it is. When the business comes to you looking for answers related to a specific incident, Appsian360 provides the quick, actionable insight necessary to provide the company with the understanding of what happened with their ERP data.
How? Appsian360 logs granular user access to data, correlates existing ERP logs, enriches the data with contextual attributes (who, when, where, what device, etc.), and visualizes the ERP data’s access and usage on dashboards. Now your team can easily look at data access by IP addresses, user IDs, location of devices, pages accessed, etc., and very quickly understand the facts behind an incident.
Let’s go back to Jim’s situation. With just a handful of clicks in Appsian360, you confirm that “Jim’s credentials” did indeed access and edit his personal information. Additionally, you discover that “Jim” was logging in after-hours using a foreign IP address based in another country. With a few more clicks, it’s clear that the IP address is responsible for other compromised user accounts. You didn’t just discover Jim’s breach, you now have a clear picture and a direction to fix the actual security issue – one that was growing in urgency by the day!
Without context, you lack insight. Context around data access and usage creates actionable insights. Actionable insights support the company and provide value to key stakeholders.
Understanding user activity and data usage are precisely what the business needs – and without Appsian360, ERP logs lack insight. You can buck that trend with Appsian360.
Contact us to learn how Appsian360 can provide you with the most powerful, real-time view into ERP data access & usage.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
SAP Access Control: A Beginner’s Guide to SAP Dynamic Authorization
As your company’s digital footprint grows, you can enhance your security posture by complementing your existing SAP Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC) with dynamic, Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC) to strengthen authentication and authorization. Both RBAC and ABAC are ways that organizations can control authentication and authorization, but they perform different functions across an enterprise IT stack.
Understanding SAP Access Control Using Roles
Functionally, a role is a collection of permissions using sets, relations, and mapping that align access needs to resources based and limit access on a “need to know” basis.
RBAC involves three basic principles:
- Role assignment: Only users with the right login can gain access to and interact with a system or application.
- Role authorization: When combined with role assignment, administrators authorize a set of credentials that can gain access to and interact with a system.
- Transaction authorization: A user can only interact with a resource to which she is authorized through her role memberships while also limited on a “need to know basis.”
RBAC has since evolved to include “hierarchies.” Hierarchies assign different roles different levels of access. For example, a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) needs to have a lot of access to sensitive information. Therefore, the CEO role has access that also encompasses the type of access provided to the Vice President’s, line of business managers, and standard employees. However, since a standard employee is at the “bottom” of the hierarchy, RBAC prevents her from accessing the sensitive information that the CEO can access.
Enhancing RBAC by Using Dynamic Authorizations in SAP
RBAC provides a strong foundation for setting access controls. However, digital transformation changes the way people interact with data resources. Since RBAC was intended for on-premises data repositories, it creates a very strict, static set of permissions. You either have access or you don’t.
Dynamic authorization – also known as attribute-based access controls (ABAC) – enhances RBAC by taking into account different “attributes.” Attributes are the adjectives of the access control world because they incorporate an additional description of either the user or resource.
Examples of user attributes:
- Department within the organization
- Management level
- Citizenship / Residency
- Security Clearance
Examples of action attributes:
- Read
- Write
- Transfer (money)
Examples of resource attributes:
- Data Classification
- Transaction Code
- Document Number
- Plant Code
Example of environment attributes:
- Time
- Geographic location
- Device type
- Connection type
By incorporating these attributes, organizations can control user access more precisely, and with the flexibility of dynamic authorizations, better balance business and security requirements.
Achieving Dynamic Access by Using Attributes
Roles act as the foundation for providing access. If you think about it like a sentence, RBAC is the subject and verb. An IT admin has what we call “superuser” access. A simple RBAC sentence might look like this:
IT administrators can read and edit all information.
Based on RBAC, this sentence provides so much access that an IT administrator could be a data breach risk. Whether maliciously stealing sensitive information or accidentally sharing private information, the unrestricted access means organizations struggle to restrict IT administrator access while still providing enough access for the employee to do their job.
However, if we add attributes, or additional descriptors about how/when/where IT administrators can use their access, we limit the risk. By creating an “if-then” statement, we apply restrictions based on the defined characteristics.
If IT administrators are accessing the database (resource attribute)
from their homes (environment attribute) then
they can read (action attribute) the information.
By adding these attributes, we can prevent IT administrators from making changes to databases while they are at home.
Furthermore, we can use attributes to grant access as well. Taking the same statement, let’s incorporate time of day as an additional attribute.
If IT administrators are accessing the database (resource attribute)
from their homes (environment attribute) then
they can read (action attribute) the information,
but if they access the database
between 8 AM and 10 AM (environment attribute 2),
they can edit user data (action attribute 2).
By adding the additional environment and action attributes, you’re creating a scenario that allows IT administrators to work from home while also reducing the risk. You have created a time-bound restriction that requires them to only make user data changes during the hours of 8 AM and 10 AM if they are at home while at all other times, they can only read the database information.
The more attributes you can incorporate, the more precisely you can define what, how, and when a user or group of users can access data.
Creating a Robust Data Security Strategy Using a Hybrid SAP Access Control Model
As organizations accelerate their digital transformation initiatives and allow more remote access to data and transactions, they need a way to configure a layered defense using a hybrid approach to SAP access control. Starting with RBAC, organizations set the foundation of their access policies. However, by incorporating different attributes such as user, resource, action, and environment characteristics, you can more appropriately limit access to and within your SAP data.
Without a solution like Appsian, the closest and organization can come to granting dynamic access to SAP is through customization or adding roles to a user for each attribute. Both options are costly and ultimately unmanageable in the long run.
Contact us to learn how Appsian can help you extend and enhance your existing SAP access controls and improve your reporting and auditing capabilities.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Does Appsian Work with SAP GRC Access Control?
At the SAPinsider 2020 virtual conference experience, one of our product demo attendees asked how Appsian works with SAP GRC Access Control. We get this question a lot as SAP security and system professionals explore adding attribute-based access controls (ABAC) to the native SAP role-based access controls (RBAC) to streamline and strengthen access policy management and enforcement. Sometimes there is confusion about whether ABAC is enhancing or replacing their RBAC. Let’s take a quick look at how Appsian’s ABAC works with and enhances SAP GRC Access Control.
What is SAP GRC Access Control
Organizations use SAP Governance, Risk, and Compliance (SAP GRC) to manage regulations and compliance and remove any risk in managing critical operations. One of the SAP GRC modules that helps organizations meet data security and authorization standards is SAP GRC Access Control. This module ensures that the right access is given to the right people with RBAC. It uses templates and workflow-driven access requests and approvals to streamline the process of managing and validating user access and provisioning. Without SAP GRC, for comparison, a person is creating all the roles from scratch and assigning privileges to them.
Appsian Enhances SAP GRC with Attribute-Based Access Controls
Appsian combines the SAP GRC role-based access controls with an attribute-based access control solution that delivers an ABAC + RBAC hybrid approach. This enhanced approach enables granular control and visibility that delivers a wide range of business benefits and lets you deploy data-centric security policies that leverage the context of access to reduce risk.
Appsian overcomes the limitations of traditional RBAC, allowing you to fully align SAP security policies with the objectives of your business and streamline audits and compliance.
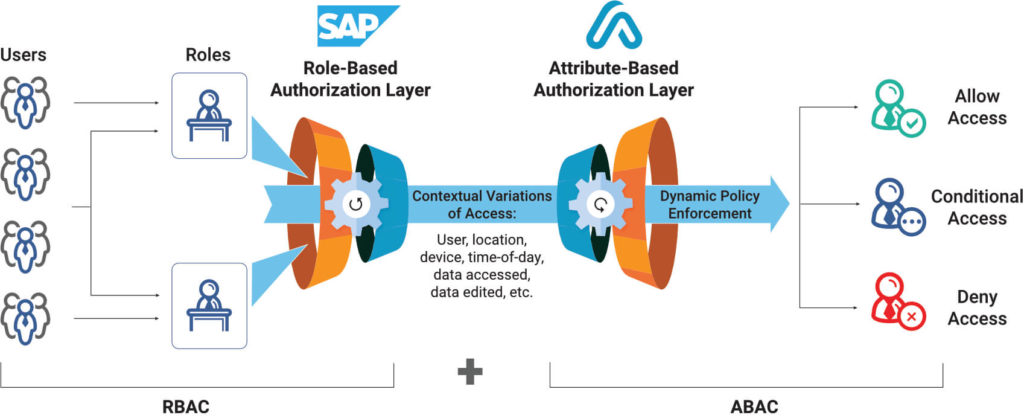
As you can see in this illustration, ABAC begins the moment users start to access data and transactions. Where RBAC assigns access based specific roles, ABAC considers the context of access (who, what, where, when, and how) before allowing access to transactions or data. Customers can set up additional rules that allow conditional access, for example, masking specific data fields or limiting the number of transactions after a particular time of day) or entirely denying access based on factors such as an unknown IP address.
Real-Time Analytics for SAP Security & Risk Management
With Appsian360, our real-time analytics and reporting tool, Appsian can enhance the SAP GRC reporting capabilities with direct, real-time visibility into transaction usage, violations, and compliance risk. Additionally, customers can:
- Monitor transaction usage, master data changes, and SoD violations
- View actual SoD violations with user, data, and transaction correlation
- Segment reports by user/data attributes
- Drill down into end-user usage events
Appsian360 provides analytical reports to drill down into end-user usage events to capture business risks and anomalies, and usage events that tie back to compliance risks.
The ABAC + RBAC Hybrid Approach to SAP GRC Access Control
By combining data-centric security capabilities with attribute-based policies, Appsian extends and enhances the existing SAP GRC internal access controls and improves the reporting and auditing capabilities.
Contact us today and schedule a demo to see how Appsian can help you enforce access controls beyond the standard RBAC model of SAP.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives