How to Reduce SoD Conflicts in SAP for Effective SOX Compliance
With several large public companies deploying SAP applications for their financial and accounting operations, ensuring SOX compliance within the SAP ecosystem is crucial for a successful audit. Segregation of Duties (SoD) in SAP plays an important role in managing roles and authorizations among SAP users to prevent conflicts and mitigate the risk of fraud.
However, user access to SAP systems is dynamic in nature due to constantly changing roles, making it challenging to track, detect, and prevent SoD conflicts. Unfortunately, SAP’s security/access management capability is static, preventing a risk-adjusted adaptive security approach recommend by Gartner. In the context of SAP, SOX compliance demands that organizations also implement an effective monitoring, alerting, and prevention mechanism for fraudulent activity arising from SoD conflicts.
How SOX Affects Internal Reporting and Controls
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act has two sections that address requirements for evidence of effective internal controls over accounting and financial reporting – sections 302 and 404. Section 302, titled: Corporate Responsibility for Financial Reports, states that the CEO and CFO are directly responsible for the accuracy, documentation, and submission of all financial reports as well as the internal control structure to the SEC. That act mandates the CEO and CFA to confirm that they accept personal responsibility for all internal controls and have reviewed these controls in the past 90 days.
While SOX section 302 defines the internal controls affecting accounting and financial reporting, SOX section 404, titled Management Assessment of Internal Controls, specifies requirements for monitoring and maintaining internal controls related to a company’s accounting and financials. Section 404 is the most complicated, most contested, and most expensive to implement of all the Sarbanes Oxley Act sections for compliance.
The Role of Access Controls for SOX 404 Compliance
Access Controls are intended to effectively manage the inherent risks associated with managing access to systems and data. These risks include segregation of duty security violations, granting excessive access, ineffective access change management process, ineffective access termination process, ineffective access review and recertification process, and poor password enforcement, to name a few.
According to Audit Standard # 5, if these types of access risks are not effectively controlled, the external SOX compliance audit will report a control issue. Control issues are ranked as a control deficiency, significant control deficiency, or worst of all, a material level control weakness. Appsian ProfileTailor GRC helps organizations effectively manage the entire SAP access management lifecycle to monitor and manage the internal control requirements of SOX sections 302 and 404.
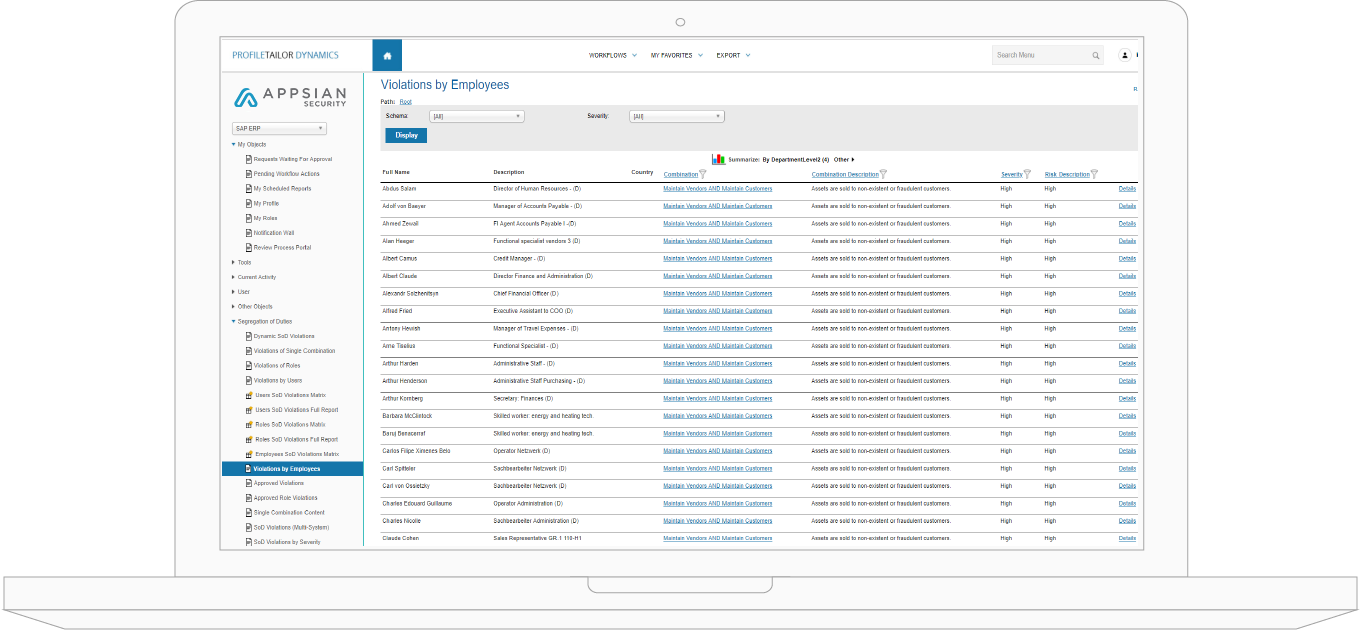
What is SoD Conflict in SAP?
Segregation of duty conflicts and SoD security violations are associated with inappropriate access at the SAP transaction workflow level. For example, an SAP user may have access to create a new vendor, create a vendor payment, and authorize that vendor payment. These three access functions should be appropriately segregated between different people because it can lead to fraud. SoD conflicts in SAP arise when user roles and the authorisations associated with those roles are not clearly defined. This leads to user over-provisining with users gaining more authortizations than required as per company policies and compliance regulations.
Overcoming SoD Conflicts in SAP for Effective SOX Compliance
To avoid access risks like SoD security violations and achieve SOX compliance in SAP, organizations need to implement the following layers of controls:
Establish effective governance and oversight of the SAP security administration process, which includes defining roles, responsibilities, policies, processes, procedures, etc., and monitoring the performance of SAP security to identify and correct performance variances quickly. Governance is often one of the most overlooked processes, and often significant SAP security administration issues occur that could have been avoided.
Establish an effective SAP security administration process for adding new users, modifying access of existing users, terminating user access in a timely manner, and performing periodic reviews of all user access for recertification. Leveraging automation, analytics, and artificial intelligence can dramatically improve the operating efficiency of the SAP security administration process. Leveraging an attribute-based access control (ABAC) security model provides more effective and adaptive security than the role-based access control model native to SAP. Additionally, ABAC can automate your SAP policy enforcement at the business process, transaction, and data level.
Internal auditors should perform an independent audit of SAP security to verify the design and effectiveness of all SAP access controls after the business unit and IT department perform their own self-assessments.
Appsian ProfileTailor GRC is a comprehensive compliance platform that enables greater control over user access risks, segregation of duties, compliance, and audit. The platform leverages embedded AI, machine learning, and predictive analytics to continuously identify potential risks and provide optimized suggestions to resolve conflicts. With Appsian, your organization can achieve SAP SOX compliance by:
- Establishing effective layers of control in governance and oversight
- Automating security administration procedures
- Implementing AI and ML empowered access risk analysis & recommendations
- Automating policy enforcement with ABAC
- Effectively monitoring and reporting with real-time analytics
- Addressing SAP security challenges with self-assessment and independent audit capabilities
Get in touch with our SAP Compliance Experts to achieve and maintain a clean SAP security environment.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Appsian Approaches Cross-Application SoD for SAP, Oracle & More
The concept of segregation of duties for SAP and other ERP applications is simple to understand: ensure that a user’s access privileges do not conflict or violate business policies and divide business processes between multiple users to limit the risk of fraud and error. However, the streamlining, managing, and enforcing of segregation of duties is far more complex. These days, organizations are turning to technology to help them automate tedious manual processes and reinforce internal controls—technology like Appsian.
Enforce Cross-Application SoD Rulesets from A Single Control Point
Appsian is a single control point that enforces cross-application SoD rules – allowing auditors and security managers to implement one SoD ruleset and enforce it on multiple applications simultaneously. They can also create rulesets for specific systems or change, activate, or deactivate SoD rules that can influence all systems together or only particular systems. Essentially, ProfileTailor GRC unifies all applications into one “language” so auditors and security managers do not have to try to understand each application’s jargon while giving them complete control over their SoD compliance, helping them comply with SOX regulations.
Maintain, Upload, and Download Rulesets in Multiple Schemas to Fit Different Scenarios
Ruleset maintenance is a focal point of any SoD implementation. ProfileTailor GRC includes various methods to create and maintain SoD rulesets easily and effectively to maximize the level of control over segregation of duties. For example, auditors can prepare a ruleset, upload it using a built-in mechanism, and then maintain the rules inside the application.
Alternatively, they can create rules in the application and then maintain, download, and upload them to Excel sheets. Further, auditors can lock specific rules for editing while allowing others to be opened. Business units can edit their own ruleset while being able only to view the organization’s global ruleset. Additionally, ProfileTailor GRC comes with a predefined ruleset that is ready for customization so organizations can be up and running almost immediately.
Resolve SoD Conflicts in Seconds
The best way to handle SoD violations is to solve them clearly and quickly. ProfileTailor GRC analyzes user behavior and usage data paired together with vast amounts of hands-on experience in the field of risk assessment to resolve SoD conflicts in just a few seconds. ProfileTailor GRC can audit violation events in real-time because it assesses SoD risks and violations based on users’ actual usage, not only on their given authorizations, and recommends the best solution for solving the violation and up to 5 additional possible solutions
Make ProfileTailor GRC a Critical Part of Your Compliance Strategies
ProfileTailor GRC can be used as a stand-alone solution for streamlining, managing, and enforcing SoD or as part of a suite of compliance products. This means that enforcing an SoD ruleset will influence other workflow processes. For example, provisioning/de-provisioning user accounts, requesting new authorizations and preventing SoD conflicts, opening new user accounts automatically without SoD violations, and business rules for granting or revoking authorization roles.
ProfileTailor GRC is compatible with all leading ERP applications, including SAP, Oracle E-Business Suite, Oracle PeopleSoft, Microsoft Dynamics, and more. It can be installed as an on-premise solution for continuous protection or in the cloud as a continuous inspection solution.
For more information on how ProfileTailor GRC approaches segregation of duties for SAP and Oracle ERPs or to receive a customized demonstration, please go HERE.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How Appsian Improves SAP Segregation of Duties Violations Management
From stopping fraud, theft, and errors to preventing SOX compliance violations, SAP Segregation of Duties (SoD) plays a lead role in minimizing business risk. Organizations must continuously iterate their internal controls to ensure their SoD strategy is effective; however, we all know this is easier said than done.
What are SoD Violations?
A Segregation of Duties or SoD violation occurs when a user has more control over a particular workflow than needed. For example, if a user can both approve new vendors and release purchase orders, it creates a conflict of interest that could, potentially, lead to fraud. The primary goal of implementing SoD is to, first, prevent users from gaining authorizations that create conflict and, second, to detect existing user authorizations that are in violation of organisational policies and/or compliance regulations.
Finite Resources & Manual Processes Can Only Address So Much
With existing capabilities, audit preparation and reporting are manually intensive processes that deliver an outdated snapshot of risk. Time and effort are wasted investigating immaterial events (i.e., false-positives, non-financial activity) because audit logs miss relevant details. Furthermore, manual analysis can be prone to errors, unscalable, and increasingly costly.
Due to resource-intensive audit processes, most organizations can only review a fraction of their SoD audit findings. This limited sample scope, typically between 3-8%, leaves the vast majority of risk unaddressed. While the sample may indicate control effectiveness, significant material risks may go undetected, and confidence will be curbed.
Leveraging Technology to Reduce Your SAP SoD Risk Exposure
Existing SAP SoD audit logs will show transaction activity but lack the data-level granularity to identify and filter out false-positive SoD violations. Manual investigation and correlation must be performed to do this – adding overhead, slowing the reporting process, and making it more difficult to prove compliance.
The bottleneck stems from technology and dictates unscalable processes. One approach to overcome this challenge is to adopt data-centric logging, which provides relevant details beyond roles and transactions – enabling customers to automate the majority of manual investigation and correlation efforts. From here, organizations can shift their valuable human resources towards remedial activities to further reduce SoD risks.
How Appsian Improves SAP Segregation of Duties Violations Management
Delivering data-centric logs paired with contextual information, Appsian360 provides visibility into SoD violations with far greater detail than what is possible with existing transaction-level audit logs. This additional information enables customers to eliminate false-positives automatically, view actual SoD violations, and prioritize events based on relevant details (e.g., dollar amount, time/location performed, etc.)
Leverage data-centric visibility to streamline SAP Segregation of Duties:
- Uncover 100% of SoD violations with data-centric continuous controls monitoring.
- Capture actionable details that would previously require manual investigation.
- Gain an always current view of SoD risks with continuous audit capabilities.
- Prioritize investigation & remediation activity by eliminating wasted effort on immaterial events.
- Simplify proving compliance with granular visibility and contextual information that is missing from existing audit logs.
- Get a Demo of Appsian360 and See for Yourself
As the burden of SAP SoD compliance grows, organizations must look towards technology to help automate tedious manual processes and strengthen internal controls. At Appsian, we’ve built our solutions with this need in mind, delivering a platform that enables SAP customers to do more with less. Contact us today for a demo, and let’s explore how we can help your organization streamline SAP segregation of duties.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives
How to Streamline the SAP Segregation of Duties Exception Process Using Attribute-Based Access Controls
Secure, compliant, and efficient business processes are critical to enterprise operations. In SAP, Segregation of Duties (SoD) is a key principle in making this possible.
What happens when an SoD exception is necessary?
Often times a user will need to be granted roles and privileges that pose a conflict of interest. It could be that an employee is part of a small department, or that a security clearance precludes others from involvement. Whatever the reason, this user needs the ability to handle multiple steps in a business process – and an exception is made.
Here’s where things can get tricky. Once an SoD exception is made, your standard preventive controls are no longer effective. This is one of the major shortfalls of SAP’s static, role-based access controls.
Shifting from a preventive approach to a detective approach…
… you must now gather access logs, filter out false-positives, and finally, send to the appropriate control owner to review and sign-off. Besides the additional overhead of manual reviews and approvals, detective controls create room for human error and increase the dwell time before red flags are caught.
So why are current SAP SoD Controls limited?
Without the logic ability to decipher potential violations from actual violations, preventive controls are a non-starter. Your (preventive) SAP access controls determine authorizations based on two things: 1.) a user’s role and 2.) the role’s associated permissions (think transactions.) While this works in the vast majority of cases, enforcing SoD requires controls with more granularity.
Let’s take a look at what an actual SoD violation entails
The whole objective of SoD is to avoid conflicts of interest in your business processes. Although, conflicting transactions do not necessarily pose a conflict of interest, unless the subject is the same.
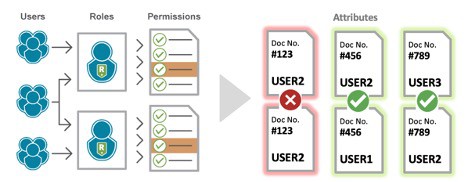
For example, a user performs the transactions to create and approve multiple purchase orders. Looking at the transactions themselves, this activity has the potential for violations. Looking deeper into the PO details, you may see that the user never created and approved the same PO – therefore no violation was made.
SAP can show you 1.) the user and role, and 2.) the transactions performed, but is missing the 3rd component: the field-level values in the PO itself. This lack of visibility into attributes beyond roles and permissions is what makes preventive controls a non-starter and clutters SoD audit logs with false-positives when exceptions have been made.
The Solution? Enforcing SoD Policy with Attribute-Based Access Controls
Attribute-Based Access Controls (ABAC) enable the use of “attributes” in authorization decisions. These attributes can be anything from user details such as role, department, nationality, or even a user’s security clearance level. Additionally, access context such as IP address, location, time, device and transaction history can be considered. And most importantly for SoD, data attributes can now be used in authorization logic. This means that field-level values within SAP can be used to determine whether to block or allow a transaction, and these details can further be used in reporting activities.
In the Purchase Order example above, data attributes can be used to identify whether a user performed the first transaction and make the correlation that performing the second transaction would result in a violation.
Combining SAP’s role-based access controls (RBAC) with an attribute-based access control (ABAC) solution enables granular control and visibility that delivers a wide range of business benefits.
Newfound Flexibility in SoD Exception Scenarios – RBAC + ABAC Hybrid Approach
The RBAC + ABAC hybrid approach opens the possibility to apply preventive controls in SoD exception scenarios. By doing so, you can offer users the flexibility an exception provides while still preventing any actual violations from happening.
Together, this hybrid approach (RBAC + ABAC) enables a dynamic SoD model that prevents violations while still allowing the flexibility of conflicting roles to be assigned (when necessary) and reinforces role-based policy to mitigate over-provisioning.
RBAC + ABAC Hybrid Approach Using Appsian
Appsian adds an additional authorization layer to SAP GRC Access Control that correlates user, data and transaction attributes, along with identified SoD conflicts, to block conflicting transactions at runtime.
Contact Us to learn more about how a hybrid access control approach can strengthen Segregation of Duties (SoD) at your organization.
Put the Appsian Security Platform to the Test
Schedule Your Demonstration and see how the Appsian Security Platform can be tailored to your organization’s unique objectives